| >> 7.1 การออกแบบสายพานโมดูล่าร์(How-To Design Modular Belt) การออกแบบสายพานโมดูล่าร์ สิ่งที่ควรรู้เมื่อต้องออกแบบสายพาน Modular 1. รูปแบบ Application 2. คุณสมบัติของวัสดุ 3. เลือกความเร็ว 4. ดูลักษณะสิ่งแวดล้อม 5. ลักษณะ Load/Unload ของวัสดุ
ข้อมูลการออกแบบ (Design Selection Process) 1. ระบบสายพานเป็นแบบวิ่งตรง/วิ่งโค้ง 2. Lay Out 3. ความเร็วในการลำเลียง 4. คุณสมบัติวัสดุ เช่น ความหนาแน่น รูปร่าง ขนาด การกัดกร่อน อุณหภูมิ ความแข็ง 5. การลำเลียงมีการเปลี่ยน Process เช่น มีการเปลี่ยน ความร้อน การหล่อเย็น การล้างทำความสะอาด 6.ได้รับการรับรองด้านสุขอนามัย 7. รูปแบบ แรงที่กระทำต่อสายพาน 8. สภาพแวดล้อมในการทำงาน 9. รูปแบบการขับ
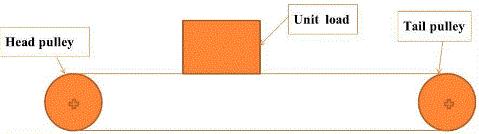
เมื่อต้องการคำนวณหาค่า Belt Pull ของสายพาน มีวิธีการดังนี้
สูตรการคำนวณค่า Belt Pull BT = (((M+2W)*Fw) + Mp)*L + (M*H) เมื่อ M = Product loading (kg/m2)
W = Belt weight, (kg/m2) (found on belt data page) L = Length of conveyor (m) H = Elevation change of conveyor (m) Fw = Wear strip belt friction coefficient Mp = Loading due to backed up product (kg/m2)
มาลองคำนวณหาค่า Belt Pull ดูหน่อย สมมติเหตุการณ์ขึ้นมาเอง มีลูกค้ารายหนึ่งต้องการให้ออกแบบสายพานที่มีระบบ Straight Running ที่ใช้ลำเลียงกล่องซึ่งให้ข้อมูลดังนี้ - น้ำหนักกล่อง 2 กิโลกรัม - กล่องที่มีพื้นที่ 0.3m x 0.3m - สายพานกว้าง 400 mm - สายพานยาว 30 m - เป็นสายพานแบบ Flat Top ในการออกแบบครั้งนี้เราจะใช้วัสดุในการผลิตสายพานคือ Polypropylene (PP) มีค่า Belt Weight = 5.2 kg/m2 และมีค่า Fw ของ UHMW = 0.13
= ( ( 22.2 + 2 * 5.2 ) * 0.13 ) *30 = 127.14 kg/m การเลือกขนาดมอเตอร์ให้เหมาะสมกับการใช้งาน เมื่อหาค่า BP และ SF ต่อไปก็จะเป็นการหาค่า Allowable Belt Strenght ดังต่อไปนี้
ABS = BS*T*S = 1155*0.95 = 1097.25 kg/m
Power = ABP*B*V/6.12 = 178*0.41*5/16.2 = 174.5 WATTS ข้อมูลจำเป็นที่ต้องใช้ในการคำนวณหาขนาดมอเตอร์ วัสดุที่ขนอะไร ขนาดของ Package ความหนาแน่นของวัตถุกี่ตัน/ลูกบาศก์เมตร ปริมาณการขนถ่ายต้องการกี่ตัน/ชั่วโมง Conveyor วางเอียงกี่องศาหรืออยู่ในแนวราบ ต้องการใช้สายพานหน้ากว้างเท่าไร ขั้นตอนการคำนวณหาขาดของมอเตอร์ STEP 1 : Determine the bake-up product load (Formula 1) STEP 2 : Calculate belt pull (BP),(Formula 2) STEP 3 : Adjusted Belt Pull ABP (Formula 3) STEP 4 : Calculate the allowable strength ABS (Formula 4) STEP 5 : Maximum spacing of drive sprockets STEP 6 : Determine drive shaft deflection STEP 7 : Drive shaft torque, T (Formula 9) STEP 8 : Belt drive power (Formula 10) STEP 9 : Determine drive motor power
Sample Problem Condition in Unit metric A beverage handle proposes to use Series 400 Raised Rib Polypropylene belting to carry steel can, weighing 122kg per square meter, on a conveyor which is 18.3 long and 1.2 wide. The belt will run wet on UHMW wear strips at a speed of 6 m per minute, frequent start under load are expected and the steel can will “Back-up” total of 15.2 m. The operating temperature is to 82 Celsius. A 12 tooth, 198 mm. pitch diameter is preferred, and carbon steel shafts are acceptable.
STEP 1 : หา Mp Mp = M * Fp (percentage of belt area Back-up /100) = 122 * 0.26 * 0.831 Mp = 26.4 kg/m^2 ค่า Fp ได้จากการเปิดหนังสือ (page 348) Belt area Back-up is (15.2/18.3)*100 = 83.1% STEP 2 : Calculate Belt Pull, BP BP = ((M+2W)*Fw+Mp)*L+(M+H) = ((122+(2*9.52))*0.11 +26.4)*18.3 BP = 767 kg/m of belt width M = Product Loading (122 kg/m^2 W = Belt weight (9.52 kg/m^2) L = Conveyor Length (18.3 m) Mp = Backed-up Product Load (26.4 kg/m^2) H = Elevation Change (Zero) STEP 3 : Adjust Belt Pull, BP (Formula 2) ABP*BP*SF ABP = 767*1.2
ABP = 920 kg/m of Belt
The service factor,SF ,determine for “Table 6 (SF)”(page 349)
STEP 4 : Calculate the allowable belt strength (ABS) ABS = BS*T*S = 3,570*0.48*1.0 = 1,714 kg/m of belt width
*****ถ้าค่า ABS ที่หาได้มีค่ามากกว่า ABP แสดงว่าสามารถใช้งานได้
STEP 5 : Maximum Spacing of drive shaft sprockets ABSU = (ABP/ABS)*100% = (920/1714)*100%
= 54% STEP 6 : Determine drive shaft deflection W = Total Shaft Load Shaft determine W = (ABS+Q)*B D = (5/384)*(W*(Ls)^3)/(E*I) W = (920+29.11)*1.2 D = 1.50 W = 1,139 kg.
***ค่าตัวแปรต่างๆที่ไม่ได้แสดงให้ดูจะอยู่ในหนังสือซึ่งมีเป็นจำนวนมากไม่สามารถนำมาลงได้หมด
STEP 7 : Drive Shaft Torque To = ABP*B*(P.D./2) To = 920*1.2*(198/2) To = 109,296 kg-mm STEP 8 : Belt Drive Power Belt Power = (ABP*B*V/6.12) Belt Power = (920*1.2*6.0/6.12) Belt Power = 1082 Watts STEP 9 : Determine Drive Motor Power Motor Power = (1082/100 – 11)*100 = 1216 Watts
Therefore a 2 kW motor will be good choice การคำนวณหาขนาดมอเตอร์ในสายพานลำเลียงตามแนวเอียง (Incline conveyor Belt) Calcolate Example Incline Conveyor The Incline conveyor system show on above picture in designed for the washing vegetables. Its vertical height is 4 m, total length of conveyor 10 m, and the belt width is 900 mm. It operate in humidity environment with the speed of 20 meter per min to transport the peas at 600 kg/m^2. The wear strips are made UHMW material, and the conveyor belt is HS-200B with 50 mm.(H) side guards. System start in condition without carrying products, and keep operating at least 7.5 hours. It adopt sprocket wit 12 teeth and stainless 38 mm*38 mm drive idle shaft. The relevant calculation formula are as follow.
STEP 1 : Calculate of unit theory tension (TB) Formula TB = {(Wp + 2WB)*FBM + WF}*L(WP * H) TB = {(60 + 2*4.4 *0.12 + 0)}*10 + (60*4) = 322.6 (kg/m) Because of it is not a piling up conveyor, WF can be ignored
STEP 2 : Calculation of unit total tension (Tw) Formula : Tw = TB * TA Tw = 322.6 * 1.6 = 516.2 (kg/m) *****Due to value TA is larger than Tw therefore HS-200BFP conveyor belt is safe and proper selection
STEP 3 : Calculation of unit allowable tension (TW) Formula : TA = BS * FS * FT TA = 980 *1.0*0.95
= 931
|




 ค่า SF (Service Factor) และค่า T (Temperature Factor) ที่ใช้ในการคำนวณ
ค่า SF (Service Factor) และค่า T (Temperature Factor) ที่ใช้ในการคำนวณ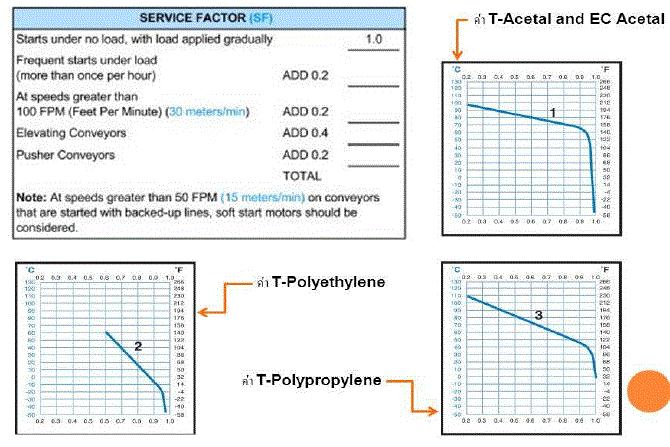
 วิธีทำ BP = ( ( M + 2W ) * L
วิธีทำ BP = ( ( M + 2W ) * L